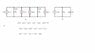
Equivalent Circuits: How Do (a) & (b) Compare?
- Thread starter Miike012
- Start date
Click For Summary
The discussion focuses on the equivalence of two electrical circuits, specifically analyzing the behavior of current i0 in a parallel configuration. It establishes that i0 is the sum of two currents flowing from a high potential to a low potential, emphasizing that the voltage remains constant across the upper and lower nodes. The conversation highlights the application of Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) and Ohm's Law to explain current distribution through resistors, asserting that the presence of a voltage source v(t) dictates the current through the resistors, regardless of other current sources in the circuit.
PREREQUISITES- Understanding of Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)
- Familiarity with Ohm's Law
- Basic knowledge of parallel circuit configurations
- Concept of voltage sources and current sources in electrical circuits
- Study the implications of Kirchhoff's Current Law in complex circuits
- Explore the behavior of ideal voltage sources and their impact on circuit analysis
- Learn about current distribution in parallel circuits with multiple sources
- Investigate advanced circuit modeling techniques using Thevenin's and Norton's theorems
Electrical engineers, circuit designers, and students studying circuit theory who seek to deepen their understanding of current behavior in parallel circuits and the principles governing voltage and current relationships.