- #1
zenterix
- 480
- 70
- Homework Statement
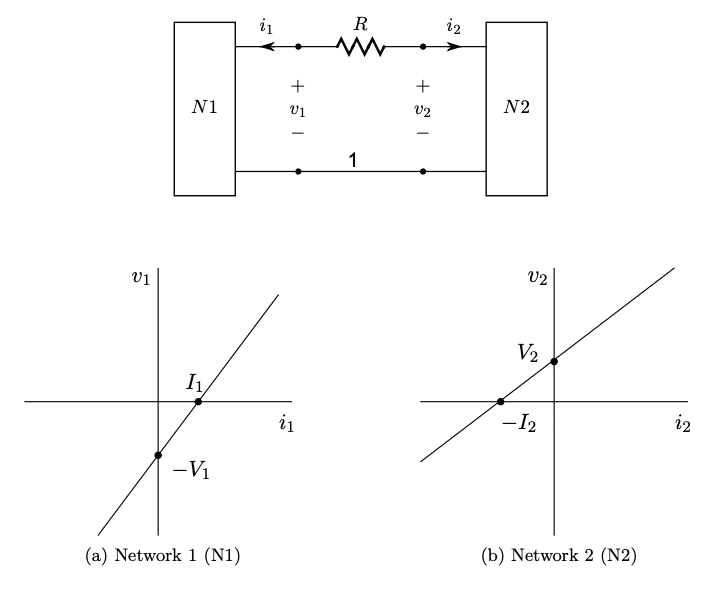
- Two networks, N1 and N2, are described graphically in terms of their ##v-i## relations, and connected together through a single resistor, as shown below
(a) Find the Thevenin and Norton equivalents of N1 and N2.
(b) Find the voltages ##v_1## and ##v_2## that result from the interconnection of N1 and N2.
- Relevant Equations
- ##v=Ri##
Thevenin equivalent network.
Norton equivalent network.
This problem is from problem set 2 of MIT OCW's 6.002 "Circuits and Electronics". There are no solutions to these problems sets, so I am posting here in case anyone spots mistakes in my solution.
Here are the two interconnected networks and their ##v-i## graphs
Here is the roadmap for this post
1) Obtain Thevenin and Norton equivalent networks for N1 going step-by-step.
2) Obtain Thevenin and Norton equivalent networks for N2 by simply inspection of the ##v-i## graph.
3) Obtain ##v_1## and ##v_2## when we interconnect N1 and N2.
Okay, starting with 1).
Here is what the Thevenin and Norton equivalent networks look like in general
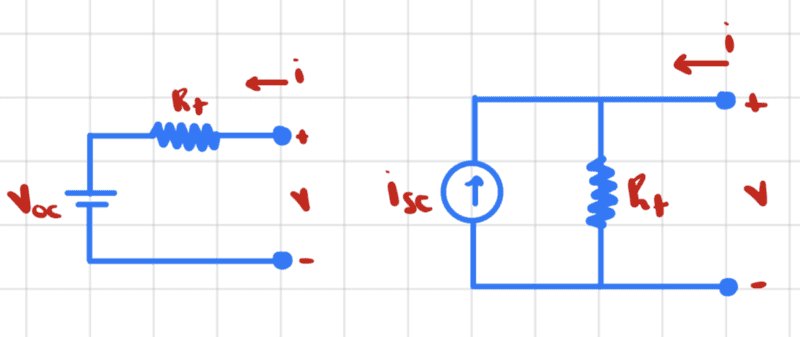
The ##v-i## relationship in the Thevenin equivalent network is
$$v=iR_t+V_{OC}\tag{1}$$
where ##V_{OC}## is the open circuit voltage between terminals + and - in the original circuit.
For the Norton equivalent network we have
$$i_{SC}+i-\frac{v}{R_t}=0\tag{2}$$
where ##i_{SC}## is the short circuit current when we short terminals + and - in the original circut.
We can solve (2) for ##v##
$$v=R_t(i+i_{SC})\tag{3}$$
and equating (1) and (3) we obtain
$$V_{OC}=i_{SC}R_t\tag{4}$$
Thus, if we find any two of ##R_t, V_{OC}##, and ##i_{SC}## then we can find the third. This allows us to easily obtain one equivalent network when we have the other.
Now, (1) and (3) give us the equations that permit us to draw graphs of ##v## as a function of ##i## for each network as is depicted in the first picture above.
Looking at it the other way around, given the graphs we can obtain the equations for the equivalent networks.
For the Thevenin equivalent network, when ##i=0## we have
$$v=V_{OC}\tag{5}$$
and when ##v=0## we have
$$i=-\frac{V_{OC}}{R_t}\tag{6}$$
For the Norton equivalent network, when ##i=0## we have
$$v=R_ti_{SC}\tag{7}$$ and when ##v=0## we have
$$i=-i_{SC}\tag{8}$$
Consider N1.
From (5) we have
$$-V_1=V_{OC}\tag{9}$$
and from (6)
$$I_1=-\frac{V_{OC}}{R_t}\tag{10}$$
Thus,
$$R_t=-\frac{V_{OC}}{I_1}=\frac{V_1}{I_1}\tag{11}$$
At this point we have ##R_t## and ##V_{OC}##, so the Thevenin equivalent network is
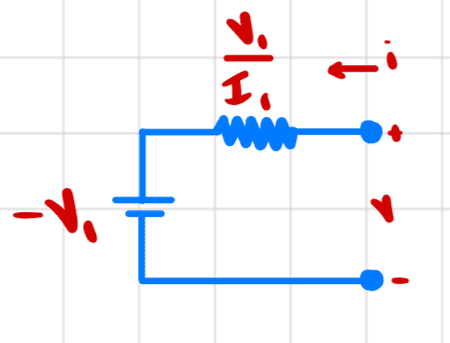
The ##v-i## relationship is
$$v=i\frac{V_1}{I_1}-V_1\tag{12}$$
Before moving on though, let me just note that this equation could have been obtained much more quickly by inspection of the graph. Then, by comparing (12) with (1) we could have identified both ##R_t## and ##V_{OC}##.
Moving on, to obtain the Norton equivalent network, first obtain ##i_{SC}## using (4)
##i_{SC}=\frac{V_{OC}}{R_t}=-I_1\tag{13}##
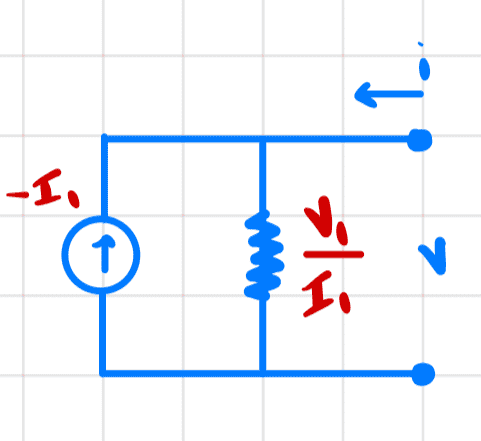
Hence, we have the Norton equivalent network
Now consider network B. Let's try to do the whole process more quickly.
The equation for the graph of the ##v-i## relationship for N2 is
$$v=V_2+\frac{V_2}{I_2}i\tag{14}$$
Hence,
$$V_2=V_{OC}=i_{SC}R_t\tag{15}$$
$$\frac{V_2}{I_2}=R_t\tag{16}$$
and so
$$i_{SC}=I_2\tag{17}$$
Hence we get the two equivalent networks
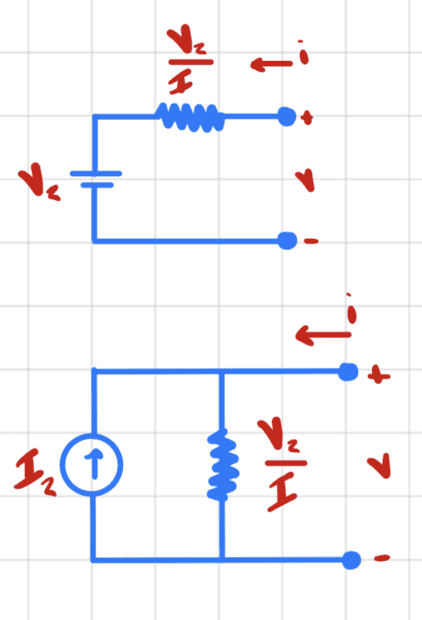
Now let's consider item (b) where we connect the two circuits.
I'm going to be honest, I'm a bit tired of typing out these equations. so I am going to paste my written calculations.
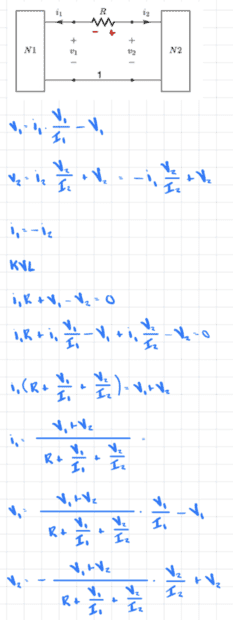
In words, we have four unknowns: ##v_1, v_2, i_1, i_2##.
KCL gives us one equation: ##i_1=-i_2##.
The ##v-i## relationships for N1 and N2 gives us two more equations.
Finally, KVL gives us one more equation.
Thus, we can solve the system.
(Just in case someone gets confused: There is a ##V_1## and a ##v_1##, and similarly for ##V_2## and ##v_2##.)
Here are the two interconnected networks and their ##v-i## graphs
Here is the roadmap for this post
1) Obtain Thevenin and Norton equivalent networks for N1 going step-by-step.
2) Obtain Thevenin and Norton equivalent networks for N2 by simply inspection of the ##v-i## graph.
3) Obtain ##v_1## and ##v_2## when we interconnect N1 and N2.
Okay, starting with 1).
Here is what the Thevenin and Norton equivalent networks look like in general
The ##v-i## relationship in the Thevenin equivalent network is
$$v=iR_t+V_{OC}\tag{1}$$
where ##V_{OC}## is the open circuit voltage between terminals + and - in the original circuit.
For the Norton equivalent network we have
$$i_{SC}+i-\frac{v}{R_t}=0\tag{2}$$
where ##i_{SC}## is the short circuit current when we short terminals + and - in the original circut.
We can solve (2) for ##v##
$$v=R_t(i+i_{SC})\tag{3}$$
and equating (1) and (3) we obtain
$$V_{OC}=i_{SC}R_t\tag{4}$$
Thus, if we find any two of ##R_t, V_{OC}##, and ##i_{SC}## then we can find the third. This allows us to easily obtain one equivalent network when we have the other.
Now, (1) and (3) give us the equations that permit us to draw graphs of ##v## as a function of ##i## for each network as is depicted in the first picture above.
Looking at it the other way around, given the graphs we can obtain the equations for the equivalent networks.
For the Thevenin equivalent network, when ##i=0## we have
$$v=V_{OC}\tag{5}$$
and when ##v=0## we have
$$i=-\frac{V_{OC}}{R_t}\tag{6}$$
For the Norton equivalent network, when ##i=0## we have
$$v=R_ti_{SC}\tag{7}$$ and when ##v=0## we have
$$i=-i_{SC}\tag{8}$$
Consider N1.
From (5) we have
$$-V_1=V_{OC}\tag{9}$$
and from (6)
$$I_1=-\frac{V_{OC}}{R_t}\tag{10}$$
Thus,
$$R_t=-\frac{V_{OC}}{I_1}=\frac{V_1}{I_1}\tag{11}$$
At this point we have ##R_t## and ##V_{OC}##, so the Thevenin equivalent network is
The ##v-i## relationship is
$$v=i\frac{V_1}{I_1}-V_1\tag{12}$$
Before moving on though, let me just note that this equation could have been obtained much more quickly by inspection of the graph. Then, by comparing (12) with (1) we could have identified both ##R_t## and ##V_{OC}##.
Moving on, to obtain the Norton equivalent network, first obtain ##i_{SC}## using (4)
##i_{SC}=\frac{V_{OC}}{R_t}=-I_1\tag{13}##
Hence, we have the Norton equivalent network
Now consider network B. Let's try to do the whole process more quickly.
The equation for the graph of the ##v-i## relationship for N2 is
$$v=V_2+\frac{V_2}{I_2}i\tag{14}$$
Hence,
$$V_2=V_{OC}=i_{SC}R_t\tag{15}$$
$$\frac{V_2}{I_2}=R_t\tag{16}$$
and so
$$i_{SC}=I_2\tag{17}$$
Hence we get the two equivalent networks
Now let's consider item (b) where we connect the two circuits.
I'm going to be honest, I'm a bit tired of typing out these equations. so I am going to paste my written calculations.
In words, we have four unknowns: ##v_1, v_2, i_1, i_2##.
KCL gives us one equation: ##i_1=-i_2##.
The ##v-i## relationships for N1 and N2 gives us two more equations.
Finally, KVL gives us one more equation.
Thus, we can solve the system.
(Just in case someone gets confused: There is a ##V_1## and a ##v_1##, and similarly for ##V_2## and ##v_2##.)
Last edited: