Homework Help Overview
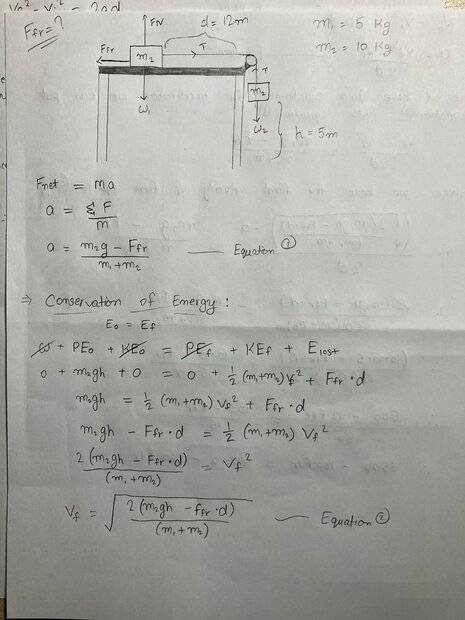
The discussion revolves around a physics problem involving the calculation of the coefficient of friction and acceleration with given masses. Participants are exploring the relationships between energy, distance, and motion in the context of a system involving a suspended mass and a block on a table.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Assumption checking, Problem interpretation
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants discuss using energy methods to find acceleration but express concerns about the plausibility of the results. Questions are raised about the problem statement, particularly regarding the distance the suspended mass drops and its implications for calculations. There is also mention of constraints on the tools available for measuring the coefficient of friction.
Discussion Status
The discussion is active, with participants clarifying the problem setup and questioning assumptions about distances and measurements. Some guidance has been offered regarding the timing of the mass drop, which may help in calculating acceleration.
Contextual Notes
Participants note that they are limited to using a meter stick for measuring the coefficient of kinetic friction and that they were not provided with the acceleration directly. There is uncertainty about whether sufficient information is available to solve the problem effectively.