SUMMARY
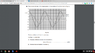
The phase difference between two oscillators can be accurately determined using the intersection points of their graphs. The correct calculation yields a phase difference of π/3 radians, as confirmed by analyzing the number of divisions between zero crossings. Each division on the graph corresponds to 0.04 seconds, and with 15 divisions representing 180 degrees, the calculation for 5 divisions results in a phase difference of 60 degrees or π/3 radians. This method emphasizes the importance of precise measurement and calculation in determining phase differences in oscillatory motion.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of oscillatory motion and phase difference
- Familiarity with graph interpretation and zero crossings
- Basic knowledge of radians and degrees conversion
- Ability to perform mathematical calculations involving fractions and ratios
NEXT STEPS
- Learn how to calculate phase differences in various waveforms
- Study the principles of harmonic motion and its graphical representation
- Explore the use of oscilloscopes for measuring phase differences
- Investigate the relationship between time and phase in oscillatory systems
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics, particularly those focusing on wave mechanics, engineers working with oscillatory systems, and educators teaching concepts of phase difference and harmonic motion.