Karl Karlsson
- 104
- 12
- Homework Statement
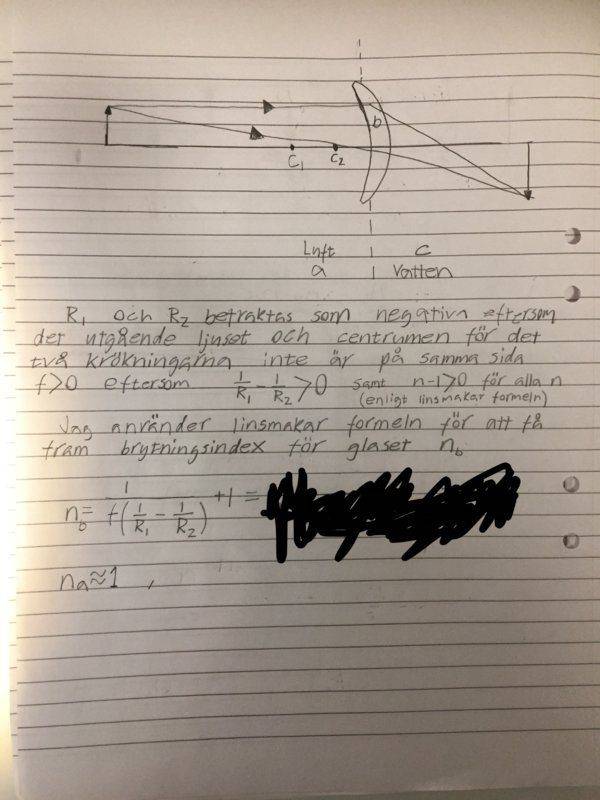
- A thin lens has an upper radius of curvature 𝑅1 and a lower radius of curvature 𝑅2. When the lens is completely surrounded by air, it has a focal distance 𝑓. The lens is then placed in the interface between air and water inside a vessel (see figure). Calculate the refractive index for the glass and the distance below the water surface on which the image of a distant object will end up?
- Relevant Equations
- A thin lens has an upper radius of curvature 𝑅1 and a lower radius of curvature 𝑅2. When the lens is completely surrounded by air, it has a focal distance 𝑓. The lens is then placed in the interface between air and water inside a vessel (see figure). Calculate the refractive index for the glass and the distance below the water surface on which the image of a distant object will end up?
A thin lens has an upper radius of curvature 𝑅1 and a lower radius of curvature 𝑅2. When the lens is completely surrounded by air, it has a focal distance 𝑓. The lens is then placed in the interface between air and water inside a vessel (see figure). Calculate the refractive index for the glass and the distance below the water surface on which the image of a distant object will end up?

The refractive index for water is given to nc = 1.33 and for air na = 1.00
My attempt:

Is my solution correct? I have nowhere to check the answer and I have not done any similar problem before. Have I missed something?
The refractive index for water is given to nc = 1.33 and for air na = 1.00
My attempt:
Is my solution correct? I have nowhere to check the answer and I have not done any similar problem before. Have I missed something?
Last edited: