Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around determining the scale factor of triangle ABC to triangle DEF, focusing on the properties of similar triangles and the implications of different definitions of scale factors and ratios. Participants explore the relationship between the perimeters and sides of the triangles.
Discussion Character
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
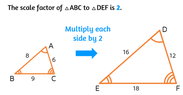
- One participant states that the perimeter of triangle ABC is 16 cm and provides the sides of triangle DEF as 6 cm, 8 cm, and 10 cm.
- Another participant calculates the scale factor based on the perimeters, suggesting a ratio of 2:3.
- One participant points out the distinction between the scale factor of triangle ABC to triangle DEF and vice versa, asserting that the scale factor should be less than 1 since triangle ABC is smaller.
- There is a question raised about the correctness of a textbook example regarding the scale factor.
- One participant claims that the dilation scale factor from triangle ABC to triangle DEF is 3/2, while also stating that the scale ratio is 2/3.
- Another participant reiterates the previous claim about the dilation scale factor and scale ratio, questioning the interpretation of "scale factor" in the original question.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the definition and calculation of the scale factor, with no consensus reached on which value is correct or what the term "scale factor" specifically refers to in this context.
Contextual Notes
There are unresolved distinctions between the terms "scale factor" and "scale ratio," as well as the implications of the triangles' sizes on the calculations. The discussion also highlights potential confusion stemming from different interpretations of similar triangles.