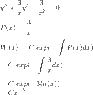SUMMARY
The discussion centers on finding the Wronskian of solutions y1 and y2 for the differential equation y'' + P(x)y' + g(x) = 0. The correct form of P(x) is identified as P(x) = 3/x, leading to the Wronskian W(x) = C x^{-3}. A critical correction is noted where the original equation must be divided by x^2 to achieve the standard form of the homogeneous equation. The final Wronskian is confirmed as accurate after revisions.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of differential equations, specifically second-order linear equations.
- Familiarity with the concept of the Wronskian in the context of linear algebra.
- Knowledge of integration techniques, particularly with logarithmic functions.
- Ability to manipulate algebraic expressions involving exponents.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of the Wronskian for different types of differential equations.
- Learn about the implications of the Wronskian in determining linear independence of solutions.
- Explore integration techniques for functions of the form exp(∫ P(x) dx).
- Review standard forms of second-order linear differential equations and their solutions.
USEFUL FOR
Students and educators in mathematics, particularly those focused on differential equations and linear algebra, will benefit from this discussion. It is also useful for anyone seeking to understand the application of the Wronskian in solving differential equations.