SUMMARY
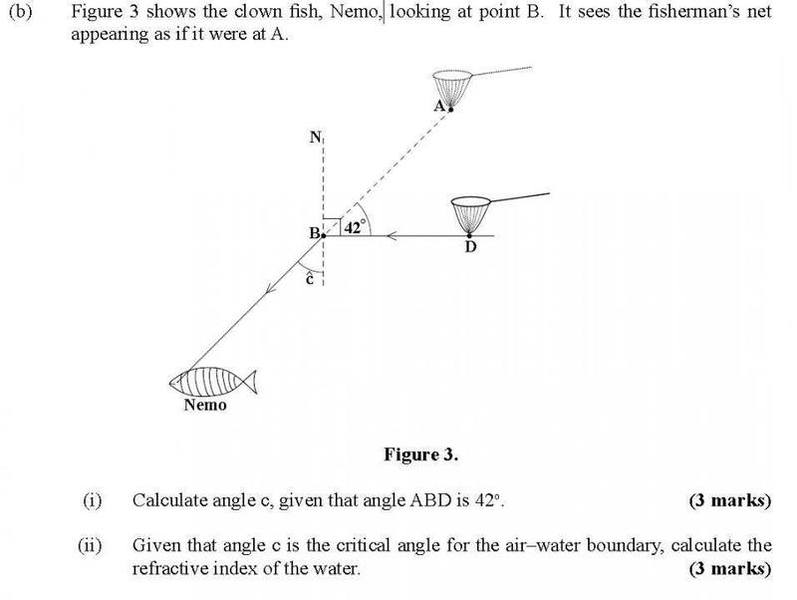
The discussion focuses on calculating the angle of refraction using Snell's Law, specifically for a scenario involving a critical angle of 48 degrees at the air-water boundary. Participants clarify that the angle of incidence is 90 degrees, leading to the conclusion that the refractive index (n) can be derived from the formula n = 1/sin(C), where C is the critical angle. The calculations confirm that the refractive index is 1/sin(48), which is essential for understanding light behavior at the interface of different media.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Snell's Law and its application in optics
- Knowledge of critical angles and refractive indices
- Basic geometry related to angles and triangles
- Familiarity with sine functions and trigonometric calculations
NEXT STEPS
- Study Snell's Law in detail, focusing on its mathematical derivation and applications
- Explore the concept of critical angles in various media, including glass and water
- Learn about the implications of refractive indices in optical engineering
- Investigate real-world applications of refraction in lenses and optical devices
USEFUL FOR
Students in physics, optical engineers, and anyone interested in the principles of light refraction and its practical applications in various fields.