dbeckam
- 8
- 1
Thread moved from the technical forums to the schoolwork forums
Summary:: Differential equation of motion, parabola
Hi. I've tried resolve this problem but I have two doubts. The first is about the differential equation of motion because I can't simplify it to the form y" + a*y' + b*y = F(t). I'm not sure if what I got is right. My second doubt is that I cannot solve part b. Thank you in advance for your help.
In part a I got this: r"(R^2 + r^2) + (r'^2)r + g*r*R = 0.
Problem:
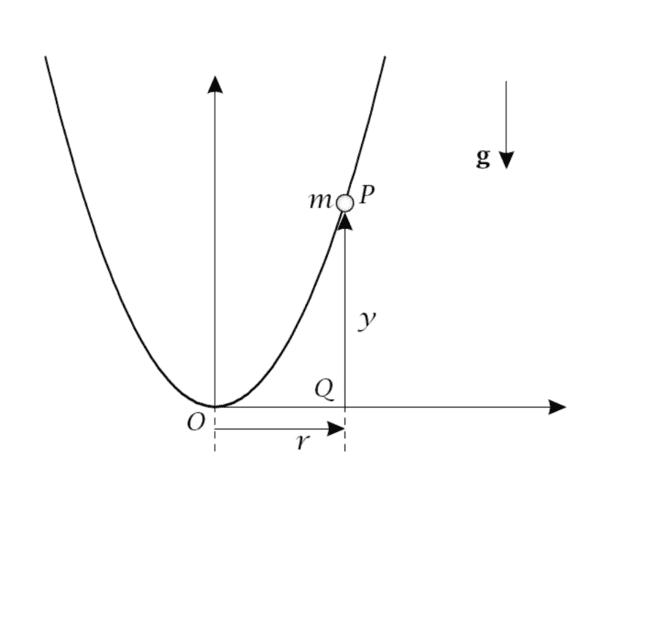
A particle of mass m slides without friction along a fixed track in the form of a parabola. The equation of the parabola is y = (r^2)/(2R). R is a constant, r is the distance between O and Q, y is the vertical distance. Initial conditions: r(t=0) = r_0 and r'(t=0) = 0.
a) Find the differential equation of motion in terms of the variable r.
b) Find an expression for (r')^2 in function of r.
Hi. I've tried resolve this problem but I have two doubts. The first is about the differential equation of motion because I can't simplify it to the form y" + a*y' + b*y = F(t). I'm not sure if what I got is right. My second doubt is that I cannot solve part b. Thank you in advance for your help.
In part a I got this: r"(R^2 + r^2) + (r'^2)r + g*r*R = 0.
Problem:
A particle of mass m slides without friction along a fixed track in the form of a parabola. The equation of the parabola is y = (r^2)/(2R). R is a constant, r is the distance between O and Q, y is the vertical distance. Initial conditions: r(t=0) = r_0 and r'(t=0) = 0.
a) Find the differential equation of motion in terms of the variable r.
b) Find an expression for (r')^2 in function of r.