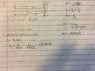SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on calculating the focal length of a lens given the distance between an object and its image, which is 28.0 cm, and a magnification of 0.550. The relevant equations are 1/f = 1/so + 1/si and M = -si/so. A critical point raised is that the image distance (si) must be treated as negative to ensure a positive magnification, which is essential for solving the problem correctly. The participants successfully resolved the issue by adjusting their understanding of the sign conventions in the equations.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of lens formulas, specifically 1/f = 1/so + 1/si
- Knowledge of magnification concepts, particularly M = -si/so
- Familiarity with sign conventions in optics
- Basic algebra skills for solving simultaneous equations
NEXT STEPS
- Review the principles of geometric optics, focusing on lens equations
- Study the concept of magnification in optical systems
- Learn about sign conventions in optics to avoid common mistakes
- Practice solving problems involving lenses and magnification
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics, particularly those focusing on optics, as well as educators looking for examples of common misconceptions in lens calculations.