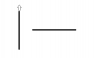- #1
megaspazz
- 13
- 0
Homework Statement
I was just wondering, so let's say there are two current carrying wires in the same plane that are perpendicular. One of them is infinite length, the other is a wire segment some distance away from the first one and perpendicular to it. What's the force on the wire segment?
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
People have been saying it's zero because the magnetic field is parallel to the wire segment, but I don't think that's true. I think that it's still perpendicular so there'll be a force on it. Am I right?