Homework Help Overview
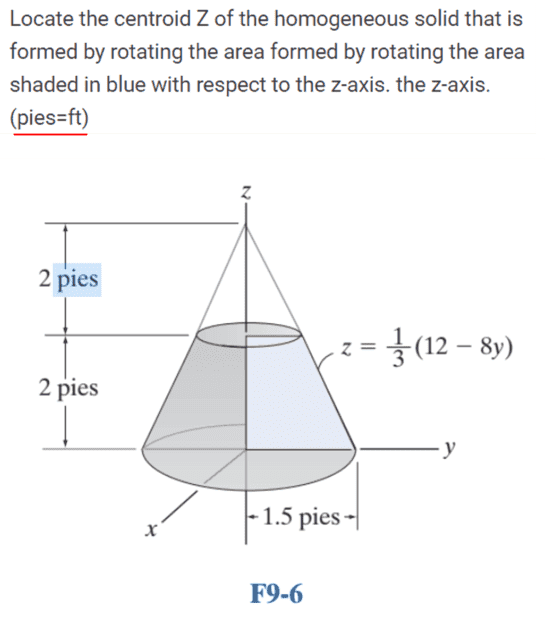
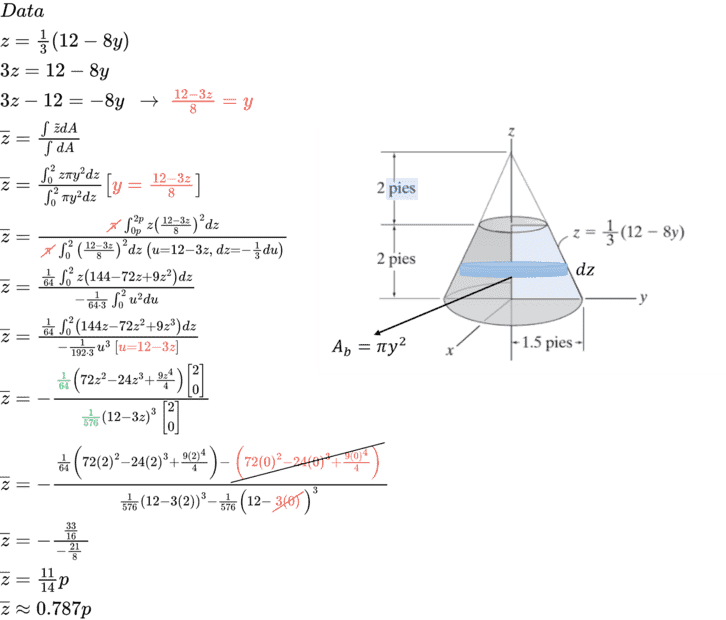
The discussion revolves around locating the coordinates of the centroid of a cone in the z-direction. Participants are exploring the necessary limits for integration and the validity of expressions related to the centroid calculation, particularly in the context of a shaded area defined in a given figure.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Assumption checking, Conceptual clarification
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants are questioning the appropriate limits for integration, specifically whether they should be from 0 to 2 or 0 to 4. There is also discussion about the validity of integrands above certain heights and the potential to solve the problem without calculus using known formulas for the centroid of a cone.
Discussion Status
The discussion is ongoing, with participants providing various insights and questioning assumptions about the volume elements contributing to the centroid calculation. Some participants express uncertainty about which formulas are acceptable to use, while others suggest that the simplest case should suffice. There is a recognition of the need to clarify concepts related to the mass center of the cone.
Contextual Notes
Participants are navigating constraints related to homework rules and the expectations of their professor regarding the use of formulas. There is a mention of the shaded area in the figure, which is critical for determining the centroid, and the need to understand the implications of the integration limits based on the geometry of the cone.