Petrus
- 702
- 0
Hello MHB,
This is an exemple I do not understand.
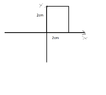
if $$R={(x,y)|-1 \leq x \leq 1, -2 \leq y \leq 2}$$, evaluate the integral
$$\int\int_R \sqrt{1-x^2}dA$$ (It is suposed to be R at down for 'rectangle' if I understand correct.)
they solve it like this $$\int\int_R \sqrt{1-x^2}dA = \frac{1}{2} \pi(1)^2 * 4 = 2\pi$$
I don't understand how they do it and
The defination says:
"If $$f(x,y) \geq0$$, then the volume V of the solid that lies above the rectangle R and below the surface $$z=f(x,y)$$ is
$$V=\int\int_R f(x,y)dA$$"
What I can note is that $$\sqrt {1-x^2} \geq0$$ and $$z=\sqrt{1-x^2} <=> x^2+z^2=1$$ so then the volume lies above the rectangle and below $$z= \sqrt{1-x^2}$$ but I get confused with dA, integrate respect to area?
Regards,
This is an exemple I do not understand.
if $$R={(x,y)|-1 \leq x \leq 1, -2 \leq y \leq 2}$$, evaluate the integral
$$\int\int_R \sqrt{1-x^2}dA$$ (It is suposed to be R at down for 'rectangle' if I understand correct.)
they solve it like this $$\int\int_R \sqrt{1-x^2}dA = \frac{1}{2} \pi(1)^2 * 4 = 2\pi$$
I don't understand how they do it and
The defination says:
"If $$f(x,y) \geq0$$, then the volume V of the solid that lies above the rectangle R and below the surface $$z=f(x,y)$$ is
$$V=\int\int_R f(x,y)dA$$"
What I can note is that $$\sqrt {1-x^2} \geq0$$ and $$z=\sqrt{1-x^2} <=> x^2+z^2=1$$ so then the volume lies above the rectangle and below $$z= \sqrt{1-x^2}$$ but I get confused with dA, integrate respect to area?
Regards,
Last edited: