karush
Gold Member
MHB
- 3,240
- 5
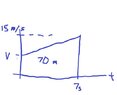
An antelope moving with constant acceleration covers the
distance between two points $\textbf{70.0m}$ apart in $\textbf{7.00s}$
Its speed as it passes the second point is $\textbf{15.00 m/s}$.
What is its speed at the first point?
The answer to this is 5 m/s
ok this should be real simple but kinda ?
$\displaystyle
\frac{70m}{7s}=\frac{10m}{s}$
so
$\displaystyle\frac{15-5}{2}=10\\
x=5$.
b. What is its acceleration
$\begin{align*}\displaystyle
a&=\frac{v_2-v_1}{t_2-t_1}\\
&=\frac{15-x}{7}\\
&\approx 1.43 m/s
\end{align*}$
kinda got it
suggestions?
distance between two points $\textbf{70.0m}$ apart in $\textbf{7.00s}$
Its speed as it passes the second point is $\textbf{15.00 m/s}$.
What is its speed at the first point?
The answer to this is 5 m/s
ok this should be real simple but kinda ?
$\displaystyle
\frac{70m}{7s}=\frac{10m}{s}$
so
$\displaystyle\frac{15-5}{2}=10\\
x=5$.
b. What is its acceleration
$\begin{align*}\displaystyle
a&=\frac{v_2-v_1}{t_2-t_1}\\
&=\frac{15-x}{7}\\
&\approx 1.43 m/s
\end{align*}$
kinda got it
suggestions?
Last edited: