CAF123
Gold Member
- 2,918
- 87
Hi,
I was trying the following question;
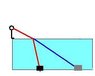
'A child of height 90 cm is standing at the edge of a 1.2m deep swimming pool. She
looks into the water and sees a brick lying on the bottom of the pool. From the
child's perspective, the brick appears to be 2.0m horizontally away from the side
of the pool. In reality, how far away is the brick from the side of the pool? (The
refractive index of water is 1.33. Assume the child's eye level is at 90 cm and the
pool is completely filled with water.)'
I know how to solve the problem, it is just I am having a little difficulty with some of the details. I took it to mean that the actual position of the brick would be the position that would be observed if there was no water, in which case it would be at the location following the straight ray (see diagram). I then took it to mean that the observed position would be at the position of the refracted ray . However, the solution has these the other way round - that is, the actual position at the refracted ray and observed position at the straight ray.( This is shown in the attachment)
Any clarification of why this is would be very helpful,
Thanks.
I was trying the following question;
'A child of height 90 cm is standing at the edge of a 1.2m deep swimming pool. She
looks into the water and sees a brick lying on the bottom of the pool. From the
child's perspective, the brick appears to be 2.0m horizontally away from the side
of the pool. In reality, how far away is the brick from the side of the pool? (The
refractive index of water is 1.33. Assume the child's eye level is at 90 cm and the
pool is completely filled with water.)'
I know how to solve the problem, it is just I am having a little difficulty with some of the details. I took it to mean that the actual position of the brick would be the position that would be observed if there was no water, in which case it would be at the location following the straight ray (see diagram). I then took it to mean that the observed position would be at the position of the refracted ray . However, the solution has these the other way round - that is, the actual position at the refracted ray and observed position at the straight ray.( This is shown in the attachment)
Any clarification of why this is would be very helpful,
Thanks.