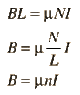SUMMARY
The magnetic field (B) inside an infinitely long solenoid is uniform and does not depend on the radius (R) of the solenoid. According to Ampère's law, the differential length (dl) is equal to L when integrated along the solenoid's length. The enclosed current (Ienc) is calculated as the product of the current (I) and the number of turns per unit length (N), leading to the conclusion that B = μ₀NI, where μ₀ is the permeability of free space. The radius does not factor into the calculation of the magnetic field inside the solenoid.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Ampère's Law
- Familiarity with magnetic fields and solenoids
- Knowledge of the permeability of free space (μ₀)
- Basic calculus for integration
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of the magnetic field inside a solenoid using Ampère's Law
- Explore the concept of magnetic field lines and their uniformity in solenoids
- Learn about the applications of solenoids in electromagnetic devices
- Investigate the effects of varying current and number of turns on the magnetic field strength
USEFUL FOR
Physics students, electrical engineers, and anyone studying electromagnetism or designing electromagnetic devices will benefit from this discussion.