- #1
mahblah
- 21
- 2
Thread moved from the technical forums to the schoolwork forums
TL;DR Summary: Find acceleration of electron in dB/dt >0
Hello. Here is a problem that i'm not so sure about:
Inside a solenoid there is a time-dipendent magnetic field B, so we have dB/dt = b (constant).
We want to know the acceleration of an electron:
a) placed in the center of the solenoid
b) displaced of r=2cm from the center
The book report that:
case a)
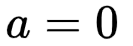
case b)
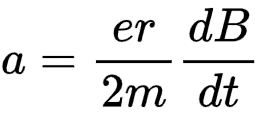
why should be different the result if the electron is placed in the center or in the displaced position? I can always imagine a "virtual circuit". Also, i think the electron "can't know where is placed".
Where am i wrong?
I've tried to solve the exercise by
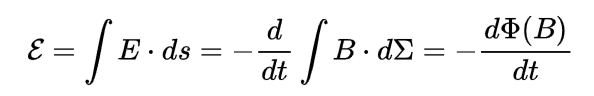
and i know i can get the result in this way:
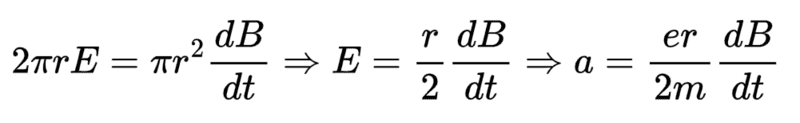
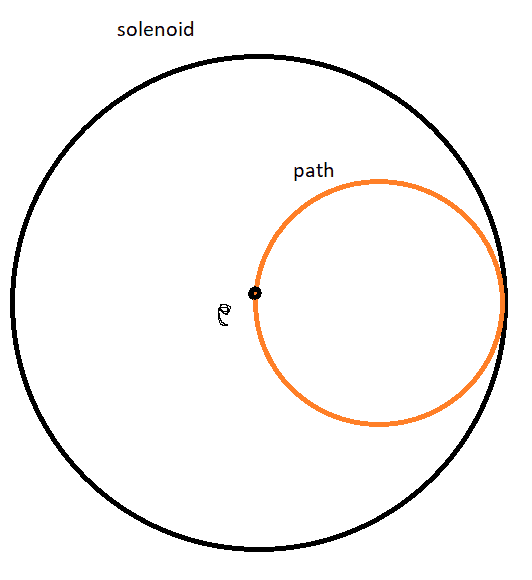
But this requires that "circle" is draw around the center.i could also draw this kind of circle (in orange) and so get a result for the electron in the center.
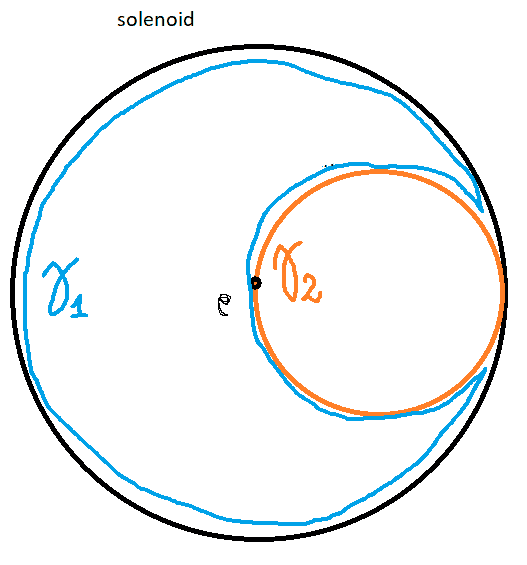
I have tried to find some answer looking for different path inside the solenoid (See below) but i'm not so convinced anyway.
 Thanks anyone
Thanks anyone
sorry for the not-so-good post.
Hello. Here is a problem that i'm not so sure about:
Inside a solenoid there is a time-dipendent magnetic field B, so we have dB/dt = b (constant).
We want to know the acceleration of an electron:
a) placed in the center of the solenoid
b) displaced of r=2cm from the center
The book report that:
case a)
case b)
why should be different the result if the electron is placed in the center or in the displaced position? I can always imagine a "virtual circuit". Also, i think the electron "can't know where is placed".
Where am i wrong?
I've tried to solve the exercise by
and i know i can get the result in this way:
But this requires that "circle" is draw around the center.i could also draw this kind of circle (in orange) and so get a result for the electron in the center.
I have tried to find some answer looking for different path inside the solenoid (See below) but i'm not so convinced anyway.
sorry for the not-so-good post.