Homework Help Overview
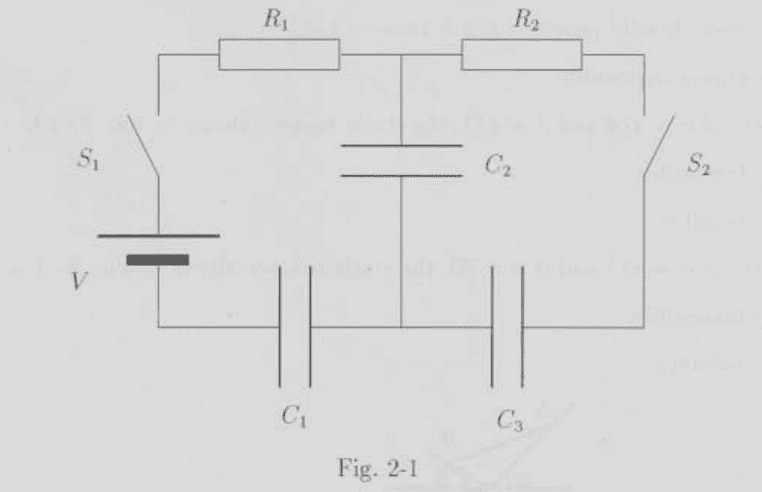
The discussion revolves around calculating the heat generated on resistor R2 after determining the voltage and charge in a circuit involving capacitors C1, C2, and C3. The problem includes concepts from circuit theory and conservation of charge.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Conceptual clarification, Mathematical reasoning, Assumption checking
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants discuss the initial conditions of the circuit, including the charging and discharging of capacitors. There are questions about the units of voltage and charge, as well as the application of conservation of charge during the redistribution of charge after closing switch S2.
Discussion Status
Some participants have confirmed their understanding of the problem setup and the conservation principles involved. There is ongoing exploration of how to apply these principles to find the relationship between charges on the capacitors before and after closing switch S2. Guidance has been provided regarding the need to clarify units and the conditions at different time points.
Contextual Notes
Participants are working under the assumption that all capacitors are initially uncharged and that the circuit configuration changes when switches S1 and S2 are manipulated. There is a focus on ensuring that the definitions and units of measurement are clear to all involved.