Nur Ziadah
- 34
- 3
- TL;DR
- I'm calculating key rate (R^Rate-wise) by integrating R(eta) over all possible eta from 0 to 1, with a probability distribution (PDTC) which is a log-normal distribution using Python language.
I'm calculating key rate (R^Rate-wise) by integrating R(eta) over all possible eta from 0 to 1, with a probability distribution (PDTC) which is a log-normal distribution.
The equation of log-normal distribution:
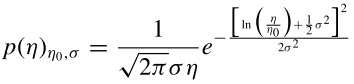
The equation of R(eta):
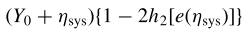
Therefore, R^Rate-wise = Integrate_0^1(R(eta)*P(eta)*d eta):
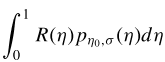
This is Python code of log-normal distribution:
This is Python code of R(eta):
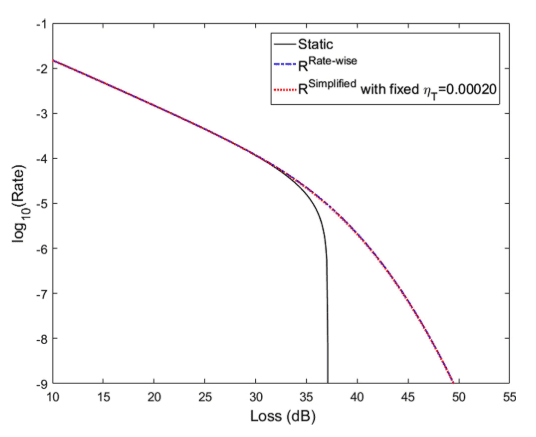
My question is how to integrate R(eta) over possible eta from 0 to 1? The output should be in the following figure (R^Rate-wise):
The referred article can be find in this link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1712.08949.pdf
Thank you so much.
The equation of log-normal distribution:
The equation of R(eta):
Therefore, R^Rate-wise = Integrate_0^1(R(eta)*P(eta)*d eta):
This is Python code of log-normal distribution:
Python:
x=np.linspace(0,1,1000)
sigma0=[0.9]
color=['green']
for i in range(len(sigma0)):
sigma=sigma0[i]
y=1/(x*sigma*np.sqrt(2*np.pi))*np.exp(-(np.log(x/0.3)+(1/2*sigma*sigma))**2/(2*sigma*sigma))
plt.plot(x,y,color[i])
plt.title('Lognormal distribution')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('lognormal density distribution')
#plt.xlim((0,0.002))
plt.ylim((0,5))
plt.show()This is Python code of R(eta):
Python:
n1=np.arange(10, 55, 1)
n=10**(-n1/10)Y0=1*(10**-5)
nd=0.25
ed=0.03
nsys=nd*n
QBER=((1/2*Y0)+(ed*nsys))/(Y0+nsys)
H2=-QBER*np.log2(QBER)-(1-QBER)*np.log2(1-QBER)
Rsp=np.log10((Y0+nsys)*(1-(2*H2)))
print (Rsp)
plt.plot(n1,Rsp)
plt.xlabel('Loss (dB)')
plt.ylabel('log10(Rate)')
plt.show()My question is how to integrate R(eta) over possible eta from 0 to 1? The output should be in the following figure (R^Rate-wise):
The referred article can be find in this link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1712.08949.pdf
Thank you so much.