SUMMARY
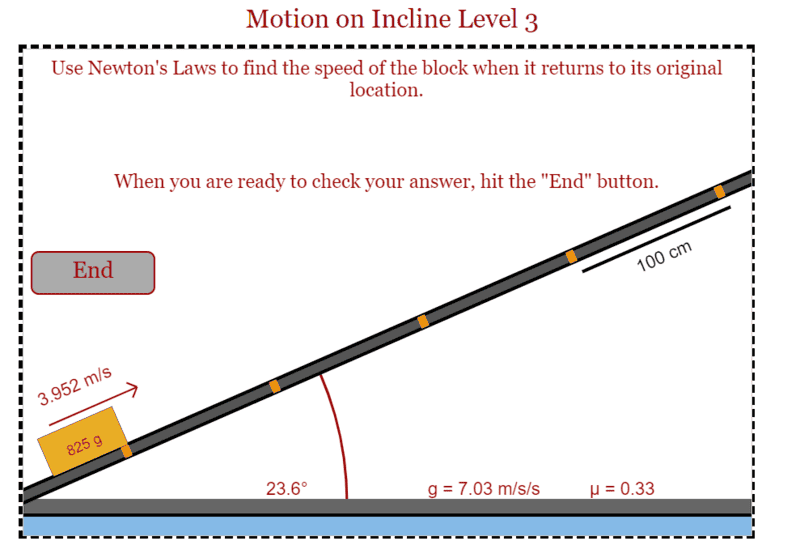
The discussion focuses on calculating the initial acceleration of a block moving up an incline, given its initial velocity. Key to solving this problem is the use of a Free Body Diagram (FBD) to analyze the forces acting on the block. The relevant equation provided is a = g sin(theta) - u g cos(theta), which must be applied carefully, considering the different phases of motion. Participants emphasize the importance of separating the up and down phases in the analysis.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Free Body Diagrams (FBD)
- Knowledge of Newton's laws of motion
- Familiarity with trigonometric functions in physics
- Basic concepts of acceleration and forces
NEXT STEPS
- Study the application of Free Body Diagrams in mechanics
- Learn about the effects of incline angles on acceleration
- Explore the derivation and application of kinematic equations
- Investigate the relationship between forces and motion in different phases
USEFUL FOR
Students of physics, educators teaching mechanics, and anyone interested in understanding motion on inclined planes will benefit from this discussion.