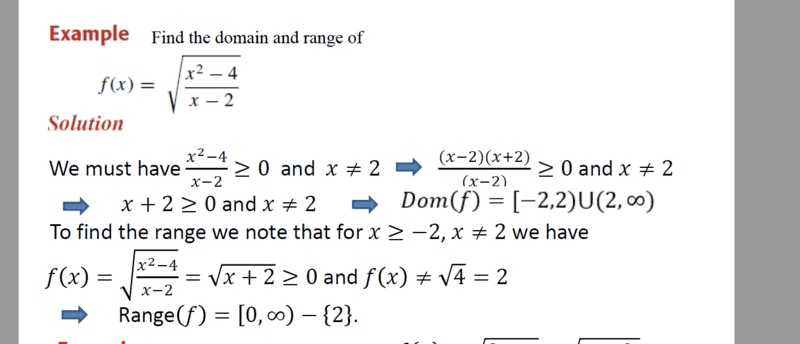Homework Help Overview
The discussion revolves around finding the range of a function involving a square root, specifically f(x) = √(x + 2) with the condition that x ≠ 2. Participants express confusion about the process of determining the range compared to the domain.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Conceptual clarification, Assumption checking
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants discuss the importance of the function's shape and monotonicity in determining the range. There are questions about the implications of the domain restriction (x ≠ 2) on the range. Some participants express uncertainty about the correct interpretation of values excluded from the range.
Discussion Status
There is an ongoing exploration of the range with some guidance provided regarding the behavior of the square root function. Participants are questioning assumptions about specific values and their inclusion in the range, but no consensus has been reached.
Contextual Notes
Participants note the specific condition that x cannot equal 2, which affects the determination of the range. There is also mention of a potential typo in the discussion regarding the value of the function at x = 2.