SUMMARY
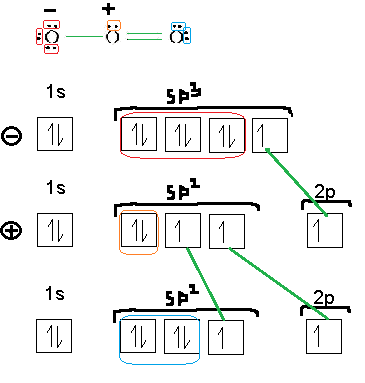
The orbital diagram presented for ozone (O3) is under scrutiny for its accuracy. The discussion emphasizes that the diagram must reflect symmetry, indicating that both outer oxygen atoms should exhibit identical hybridizations. The inclusion of bonds and lone pairs in color is noted, but the correctness hinges on maintaining consistent hybridization across the molecule.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of molecular orbital theory
- Familiarity with hybridization concepts
- Knowledge of ozone's molecular structure
- Ability to interpret orbital diagrams
NEXT STEPS
- Research the hybridization of ozone (O3) and its implications on molecular symmetry
- Study molecular orbital diagrams and their representations for diatomic and triatomic molecules
- Explore the concept of resonance structures in ozone
- Learn about the role of lone pairs in determining molecular geometry
USEFUL FOR
Chemistry students, educators, and professionals involved in molecular modeling or studying molecular geometry will benefit from this discussion.
 Thanks in advance.
Thanks in advance.