SUMMARY
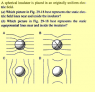
The discussion focuses on the behavior of a dielectric sphere placed in a homogeneous electric field, specifically addressing the correctness of options A and C, which represent electric field lines and equipotential lines, respectively. Participants confirm that electric field lines cannot intersect, eliminating option B, and establish that the induced dipoles within the dielectric sphere create surface charges that oppose the external field. The relationship between the electric field inside and outside the sphere is clarified, emphasizing that the electric field inside the sphere is weaker and that the field lines remain parallel to the external field due to boundary conditions.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of electric field lines and equipotential lines
- Knowledge of dielectric materials and their polarization
- Familiarity with boundary conditions in electrostatics
- Basic concepts of electric displacement vector (D) and its components
NEXT STEPS
- Study the behavior of dielectrics in electric fields using "Introduction to Electrodynamics" by David J. Griffiths
- Learn about the mathematical representation of electric field lines and equipotential surfaces
- Explore the concept of polarization in dielectrics and its effects on electric fields
- Review boundary conditions in electrostatics and their implications on electric fields
USEFUL FOR
Students and educators in physics, particularly those studying electromagnetism, as well as engineers working with dielectric materials in electric fields.