- #1
buildingblocs
- 17
- 1
Hi All,
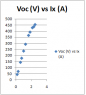
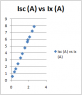
Today I conducted a lab in which we plotted the open circuit voltage (V[oc]) and closed circuit current (I[sc]) versus the excitation current in the rotor (I[x]).
From the data (plots are attached to thread), it can be seen that saturation occurs in the V[oc] versus I[x] curve however the I[sc] versus I[x] curve remains linear.
Why is it that saturation occurs only with V[oc] and not with I[oc] in the stator?
Today I conducted a lab in which we plotted the open circuit voltage (V[oc]) and closed circuit current (I[sc]) versus the excitation current in the rotor (I[x]).
From the data (plots are attached to thread), it can be seen that saturation occurs in the V[oc] versus I[x] curve however the I[sc] versus I[x] curve remains linear.
Why is it that saturation occurs only with V[oc] and not with I[oc] in the stator?