Memocyl
- 3
- 0
Hello friends (I hope  ),
),
For a maths project I am working on, I need to be able to prove the equation for an elliptical orbit, related to Kepler's first law:
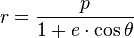 and p = a(1-e2) (or should be as p can be replaced by that value)
and p = a(1-e2) (or should be as p can be replaced by that value)
Where:
r = distance from sun to any point on the orbit
p = semi latus rectrum
a = semi-major axis
e = eccentricity
θ = true anomaly (angle between a and r anticlockwise I think)
Can someone please help me to understand where these equations come from and also confirm that I have got my current facts straight?
Regards,
Memocyl
For a maths project I am working on, I need to be able to prove the equation for an elliptical orbit, related to Kepler's first law:
Where:
r = distance from sun to any point on the orbit
p = semi latus rectrum
a = semi-major axis
e = eccentricity
θ = true anomaly (angle between a and r anticlockwise I think)
Can someone please help me to understand where these equations come from and also confirm that I have got my current facts straight?
Regards,
Memocyl