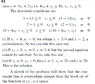- #1
Rabolisk
- 6
- 0
Hello I have a worked example where I have to maximize a function with an inequality constraint. The problem is worked out below.
https://zgqqmw.sn2.livefilestore.com/y1pLc13HVWpA9dATZEzikySeSMBN2hn1mJCw71rJ5vvUJcr9W7KBPFkOz7HQEppa6EPbLi5yyAwDagh3ezF_7eyVL6tBK7q6ise/maxProbem.png?psid=1
I know how to get the kuhn-tucker conditions in the first step. I also understand how the first two possibilities (i) and (ii) are ruled out. In the third one the value of [itex]\lambda[/itex] is 2. But how did the problem work out the value of and x2 to be 10?
Thanks.
https://zgqqmw.sn2.livefilestore.com/y1pLc13HVWpA9dATZEzikySeSMBN2hn1mJCw71rJ5vvUJcr9W7KBPFkOz7HQEppa6EPbLi5yyAwDagh3ezF_7eyVL6tBK7q6ise/maxProbem.png?psid=1
I know how to get the kuhn-tucker conditions in the first step. I also understand how the first two possibilities (i) and (ii) are ruled out. In the third one the value of [itex]\lambda[/itex] is 2. But how did the problem work out the value of and x2 to be 10?
Thanks.
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: