ryeager
- 2
- 0
Hi, thanks in advance to all who help
a) Determine the time constant for charging the capacitor in the circuit given.
b) what is the maximum charge on the capacitor?
R1
______vvvv____________
| | |
| < |
E R2 > C
| | |
|______________|______|
E = emf and C is the capacitor, sorry for the poor illustration.
Mentor's edit: Here's a better illustration:
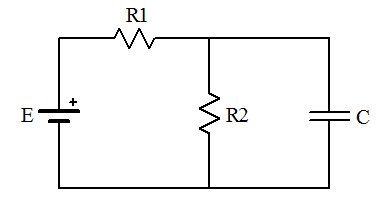
For a, I've determined the equivalent resistance of parallel resistors to be (1/R1 + 1/R2)^-1 = R1R2/(R1+R2), thus the time constant would be tau = CReq = CR1R2/(R1+R2)
For b) I have a feeling Qmax for the capacitor will be Qmax = CV where V is the voltage across R2 since R2 and C are parallel, but I can't figure out V across R2 in terms of E, R1, R2, C. Can anyone help? Thanks again.
a) Determine the time constant for charging the capacitor in the circuit given.
b) what is the maximum charge on the capacitor?
R1
______vvvv____________
| | |
| < |
E R2 > C
| | |
|______________|______|
E = emf and C is the capacitor, sorry for the poor illustration.
Mentor's edit: Here's a better illustration:
For a, I've determined the equivalent resistance of parallel resistors to be (1/R1 + 1/R2)^-1 = R1R2/(R1+R2), thus the time constant would be tau = CReq = CR1R2/(R1+R2)
For b) I have a feeling Qmax for the capacitor will be Qmax = CV where V is the voltage across R2 since R2 and C are parallel, but I can't figure out V across R2 in terms of E, R1, R2, C. Can anyone help? Thanks again.
Last edited by a moderator: