dvolpe
- 34
- 0
Homework Statement
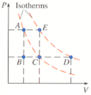
. Suppose a monatomic ideal gas is changed from state A to state D by one of the processes shown on the PV diagram below, in which each interval on the vertical (P) axis corresponds to 2 atm, and the values of the lines on the horizontal (V) axis equal 1 L, 2 L, and 4 L.
Graph attached.
(a) Find the total work done on the gas if it follows the constant volume path A-B followed by the constant pressure path B-C-D.
(b) Find the total change in internal energy and total heat flow into the gas.
Homework Equations
For isotherm W = nRt (ln (Vf/Vi)
PV = nRT
The Attempt at a Solution
From A to B to C is an isotherm. Use equation above but substitute PV for nRT for either A or C as they are the same - got 255.6 J. Then add in PdeltaV for C to D as on 2 different isotherms. Total work = A to C isotherm work plus C to D work = 655.6. HELP!