- #1
QuarkDecay
- 47
- 2
- TL;DR Summary
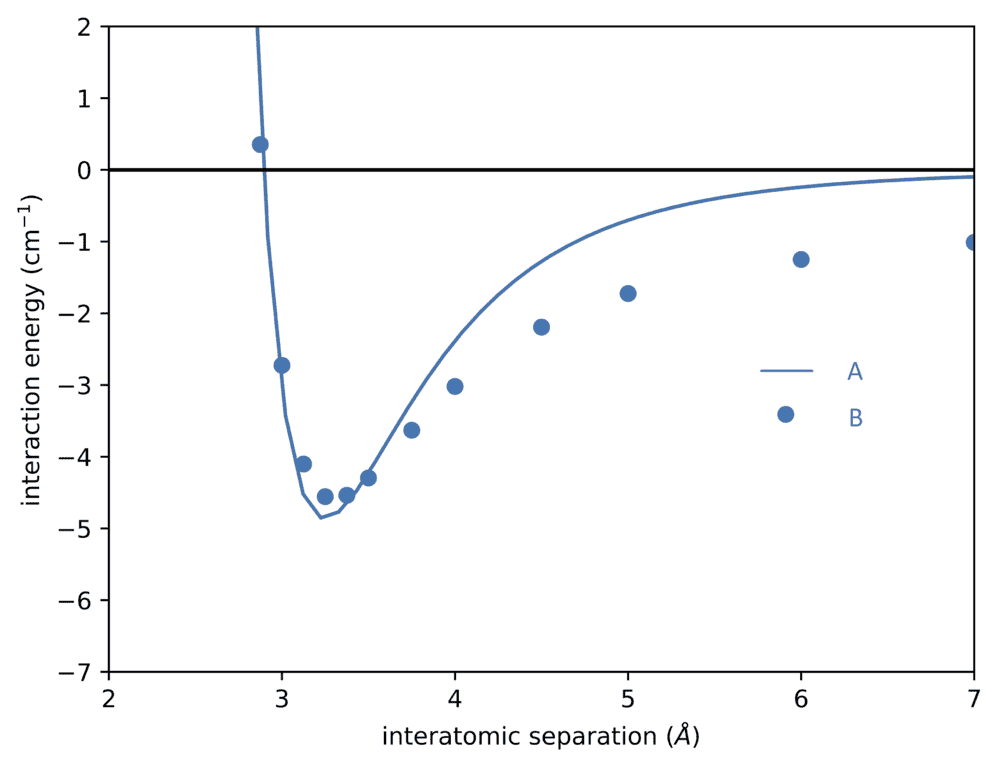
- Two Morse potential like below are given. What are their energy eigenvalues?
I know the eigen value of energy in a Morse potential is
Evib= ħωo(v+ 1/2) - ħωoxe(v+ 1/2)2
but is this the same for every Morse potential, given that the masses μ of the diatomic molecules are the same?
The two potentials are these:
Evib= ħωo(v+ 1/2) - ħωoxe(v+ 1/2)2
but is this the same for every Morse potential, given that the masses μ of the diatomic molecules are the same?
The two potentials are these: