HapaxOromenon
- 3
- 0
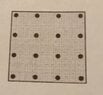
Consider a dotted square grid with $4$ rows and $4$ columns, as shown: View attachment 9092
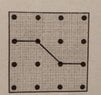
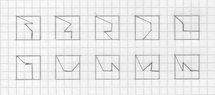
By drawing a series of connected straight lines from dot to dot, it is possible to divide the square (which effectively has side length $3$) into two parts of equal area. One way of doing this is as shown: View attachment 9093
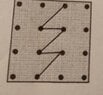
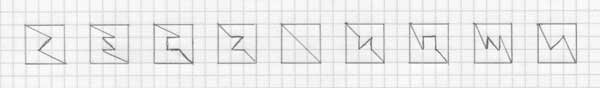
Other examples of ways of doing this are: View attachment 9094; View attachment 9095; and View attachment 9096.
The question I am investigating is how many such ways there are in total, or if such a calculation is too difficult, I would at least like to have a systematic way of listing all of the ways. But I'm not sure really where to start. Any assistance would be greatly appreciated.
By drawing a series of connected straight lines from dot to dot, it is possible to divide the square (which effectively has side length $3$) into two parts of equal area. One way of doing this is as shown: View attachment 9093
Other examples of ways of doing this are: View attachment 9094; View attachment 9095; and View attachment 9096.
The question I am investigating is how many such ways there are in total, or if such a calculation is too difficult, I would at least like to have a systematic way of listing all of the ways. But I'm not sure really where to start. Any assistance would be greatly appreciated.