SireJeff
- 2
- 0
- TL;DR
- my question is about understanding origin of centripetal force when the net force towards the center is zero and I got this issue from a homework which I solved but quite have a problem understanding the concept ,for a body of mass with little to no rotation, if it starts moving on the surface of a circle like hill with radius R, what other forces beside Normal and gravitational are applied to it to count for centripetal Force when N and Fg counteract each other completely
to clarify , my purpose isn't to find a solution to my home work , I already did the home work and my thread is more a request of justification or at least a clarification of the forces at play. I need explanation on the general topic not the solution to my question, I am mentioning the question and trying to use it as a way to further develop and explain the context of my problem .
I have this question about centripetal force of an object rolling down a hill . so here's he question:
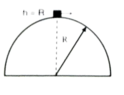
"A mass m is released from the top of a vertical circular track of radius r with a horizontal speed v0. Find angle θ where it leaves the contact with circular track.(object is dense and small, no rotation ,no friction no preliminary acceleration, the object starts moving slowly from the top)"
Now I know how to calculate for it but I don't get the presuppositions that we have for this object. The first idea that came into my head was that I should equate the sum of of N and Fg(force of gravity) forces along the y axis to the centripetal force(mV^2/R) and continue from there.
But I have this problem with the supposition , if the nromal force is the reaction of the surface to the force of gravity towards the mass of the object, then if Fg along the y axis is Fg=m.g.cos(theta) ,the normal force has to be the same as it ,then what force is acting as the centripetal force if the net force along the y axis equals zero?
Yet again I know since it's moving along a circle with Radius R, there has to be a force which is puling it inwards towards the center perpendicular to the velocity(direction of displacement) , I just can not understand what originates it, also I have to mention I'm modeling this in cartesian co-ordinates
[Thread edited some by the Mentors for readability]
I have this question about centripetal force of an object rolling down a hill . so here's he question:
"A mass m is released from the top of a vertical circular track of radius r with a horizontal speed v0. Find angle θ where it leaves the contact with circular track.(object is dense and small, no rotation ,no friction no preliminary acceleration, the object starts moving slowly from the top)"
Now I know how to calculate for it but I don't get the presuppositions that we have for this object. The first idea that came into my head was that I should equate the sum of of N and Fg(force of gravity) forces along the y axis to the centripetal force(mV^2/R) and continue from there.
But I have this problem with the supposition , if the nromal force is the reaction of the surface to the force of gravity towards the mass of the object, then if Fg along the y axis is Fg=m.g.cos(theta) ,the normal force has to be the same as it ,then what force is acting as the centripetal force if the net force along the y axis equals zero?
Yet again I know since it's moving along a circle with Radius R, there has to be a force which is puling it inwards towards the center perpendicular to the velocity(direction of displacement) , I just can not understand what originates it, also I have to mention I'm modeling this in cartesian co-ordinates
[Thread edited some by the Mentors for readability]
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: