Lambda96
- 233
- 77
- Homework Statement
- Calculate the following limits ##\displaystyle{\lim_{n \to \infty}} p^n## and ##\sum\limits_{k=0}^{\infty} p^k##
- Relevant Equations
- none
Hi,
I'm not sure if I have calculated the task here correctly
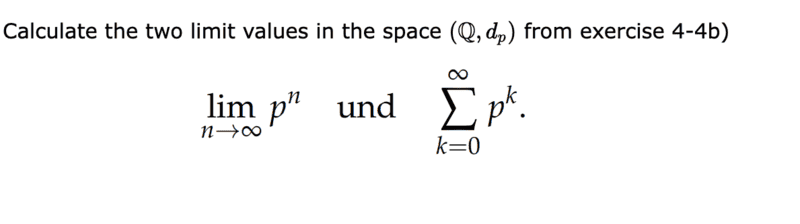
Task 4-4b looked like this
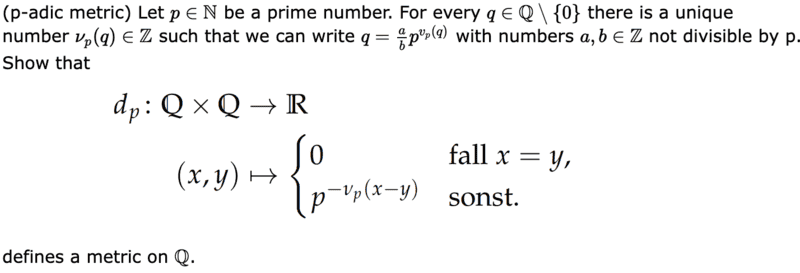
I have now obtained the following with ##n=-v_p(x-y)##
$$\displaystyle{\lim_{n \to \infty}} p^n= \infty$$
$$\sum\limits_{n=0}^{\infty} p^n=\frac{p}{p-1}$$
Is that correct?
I'm not sure if I have calculated the task here correctly
Task 4-4b looked like this
I have now obtained the following with ##n=-v_p(x-y)##
$$\displaystyle{\lim_{n \to \infty}} p^n= \infty$$
$$\sum\limits_{n=0}^{\infty} p^n=\frac{p}{p-1}$$
Is that correct?