Hypersphere
- 189
- 8
Hi,
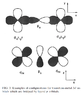
Reading http://rmp.aps.org/abstract/RMP/v70/i4/p1039_1 I've run into a notational question of atomic p orbitals. The authors use symbols like p_\sigma and p_\pi. From their fig. 3 (attached), they do look like p_x and p_z orbitals, respectively, rather than anything close to σ or π bonds.
Is this just a common notational convention that I've somehow missed? And if so, what is the symbol for the third p orbital?
Reading http://rmp.aps.org/abstract/RMP/v70/i4/p1039_1 I've run into a notational question of atomic p orbitals. The authors use symbols like p_\sigma and p_\pi. From their fig. 3 (attached), they do look like p_x and p_z orbitals, respectively, rather than anything close to σ or π bonds.
Is this just a common notational convention that I've somehow missed? And if so, what is the symbol for the third p orbital?