sameeralord
- 659
- 3
Hello everyone  ,
,
I'm so confused with particle displacement vs time graph and pressure vs time graph of sound. I thought maximum displacement of a particle is its compression and minimum displacement is its rarefaction. For some strange reason the graphs show exactly the opposite. How can the particles be at atmospheric pressure when the displacement is maximum. Your help would be greatly appreciated. Thanks
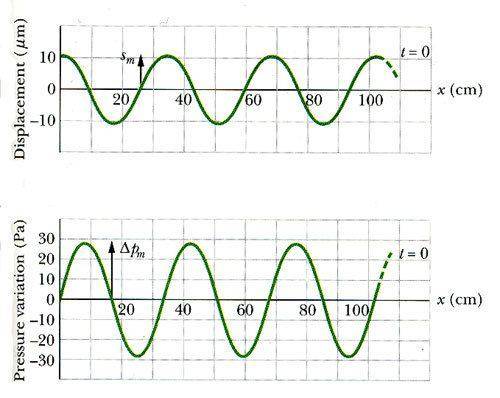
I'm so confused with particle displacement vs time graph and pressure vs time graph of sound. I thought maximum displacement of a particle is its compression and minimum displacement is its rarefaction. For some strange reason the graphs show exactly the opposite. How can the particles be at atmospheric pressure when the displacement is maximum. Your help would be greatly appreciated. Thanks