Discussion Overview
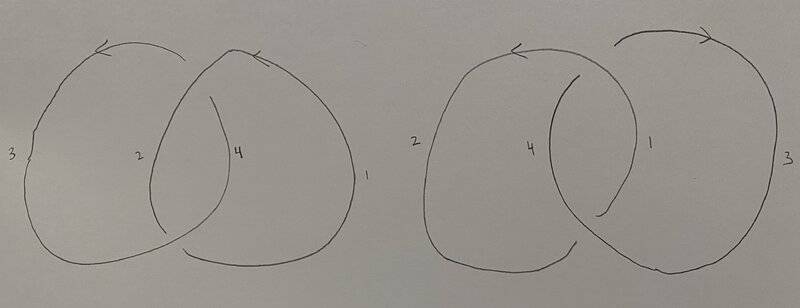
The discussion revolves around the interpretation of a particular PD code, specifically [(2, 3, 1, 4), (4, 1, 3, 2)], and its mapping to knot diagrams. Participants explore the implications of this code in relation to knot theory, particularly focusing on whether it yields a unique knot diagram or multiple representations, including links.
Discussion Character
Main Points Raised
- One participant asserts that the PD code maps to a non-unique knot diagram, presenting two Hopf links with different orientations as examples.
- Another participant questions whether the diagrams in question are indeed knots, suggesting they resemble interconnected rings instead.
- A third participant clarifies that the PD code corresponds to a unique link diagram, stating that the Hopf link is valid and noting that a ring is considered the unknot.
- One participant offers a suggestion to manipulate one of the rings to potentially clarify the situation.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on whether the PD code leads to a unique knot diagram or multiple representations. There is no consensus on the nature of the diagrams as knots or links.
Contextual Notes
There are unresolved assumptions regarding the definitions of knots and links, as well as the implications of the PD code in this context.