SUMMARY
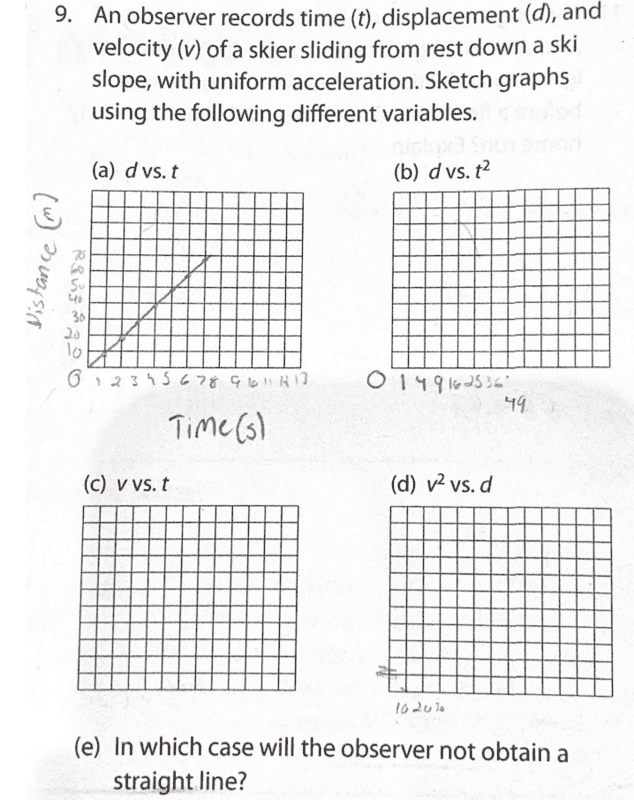
The discussion focuses on solving a physics problem involving the motion of a skier down a slope, specifically using the equations of motion under uniform acceleration. Key concepts include the use of the SUVAT equations, particularly the equation d = 0.5at^2, where d represents displacement, a is acceleration, and t is time. The gravitational acceleration of 9.8 m/s² is mentioned, but it is clarified that the skier's acceleration may differ since they are not in free fall. Participants emphasize the importance of plotting graphs based on the derived equations to visualize the skier's motion.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of basic kinematics and motion equations
- Familiarity with the SUVAT equations
- Knowledge of graphing techniques for mathematical functions
- Concept of uniform acceleration in physics
NEXT STEPS
- Study the SUVAT equations in detail, focusing on their applications in various motion scenarios.
- Learn how to derive and manipulate the equation
d = 0.5at^2 for different values of acceleration.
- Practice graphing quadratic functions to represent motion under uniform acceleration.
- Explore the effects of varying acceleration on displacement and velocity in real-world scenarios.
USEFUL FOR
This discussion is beneficial for physics students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the principles of motion and graphing techniques in kinematics.