SUMMARY
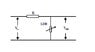
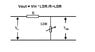
The formula Vout = Vin * R2/(R1+R2) calculates the output voltage (Vout) in a voltage divider circuit, where Vin is the input voltage, R1 is the first resistor, and R2 is the second resistor. In practical applications, when a load resistor (R3) is connected to Vout, the effective resistance changes, necessitating the use of the modified formula Vout = Vin * R2||R3 / (R1 + R2||R3) to accurately determine Vout. For example, with Vin at 12V, R1 at 10 ohms, R2 at 5 ohms, and R3 at 2 ohms, Vout calculates to 1.5V. The discussion emphasizes the importance of considering load resistance in circuit analysis for accurate voltage predictions.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of voltage divider circuits
- Familiarity with Ohm's Law
- Knowledge of parallel resistor calculations
- Basic circuit analysis skills
NEXT STEPS
- Study the concept of load resistance in voltage dividers
- Learn about operational amplifiers and their input impedance
- Explore the effects of varying resistor values on output voltage
- Investigate the impact of source resistance on voltage dividers
USEFUL FOR
Electronics students, circuit designers, and engineers looking to deepen their understanding of voltage dividers and load effects in electrical circuits.