ctownballer03
- 8
- 0
Suppose X and Y are independent Poisson random variables with respective parameters λ and 2λ.
Find E[Y − X|X + Y = 10]3: I had my Applied Probability Midterm today and this question was on it. The class is only 14 people and no one I talked to did it correctly. The prof sent out an e-mail saying how no one did it correctly and we need to work on it and get it figured out and corrected by our next class and frankly I'm still super stuck (my professor is pretty useless, I can't utilize him as resource for anything in this class). Anyways, this is my attempt at doing this however I realize that I've made a mistake and even though X and Y are independent, Y=y and X+Y=10 are NOT independent events so the cancellation that I did is not a legal move.. Any other ideas of how to approach this problem, I feel like I'm back to square one and I'm not sure where to go. Thank you!
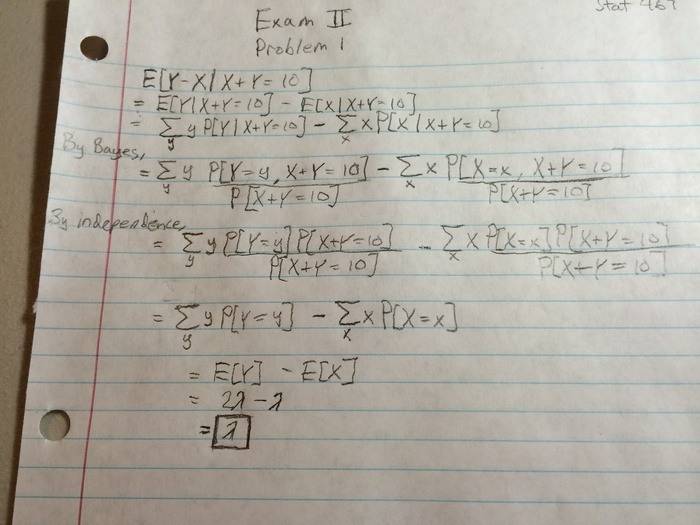
Find E[Y − X|X + Y = 10]3: I had my Applied Probability Midterm today and this question was on it. The class is only 14 people and no one I talked to did it correctly. The prof sent out an e-mail saying how no one did it correctly and we need to work on it and get it figured out and corrected by our next class and frankly I'm still super stuck (my professor is pretty useless, I can't utilize him as resource for anything in this class). Anyways, this is my attempt at doing this however I realize that I've made a mistake and even though X and Y are independent, Y=y and X+Y=10 are NOT independent events so the cancellation that I did is not a legal move.. Any other ideas of how to approach this problem, I feel like I'm back to square one and I'm not sure where to go. Thank you!