Discussion Overview
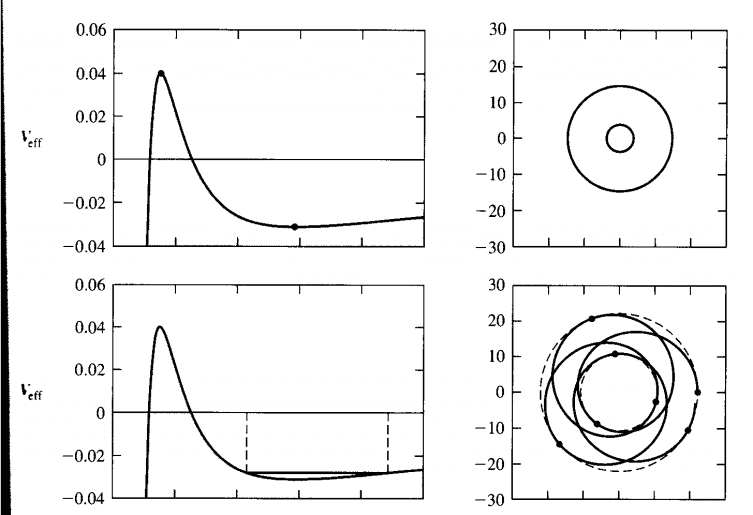
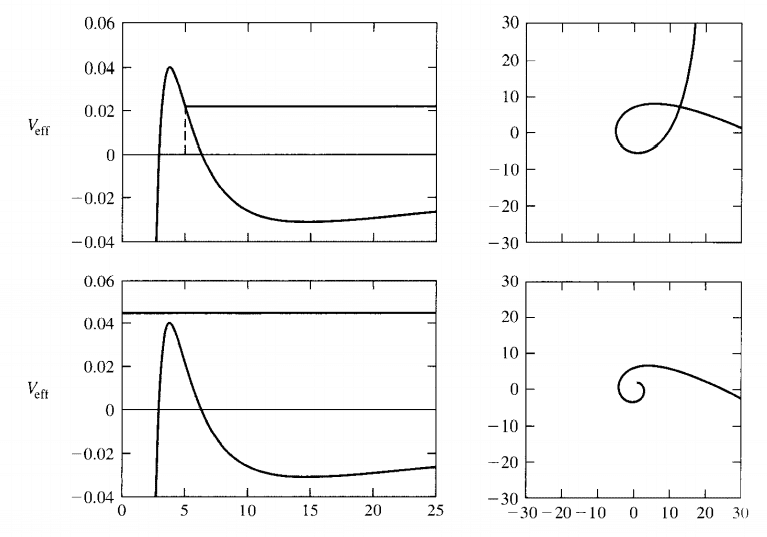
The discussion revolves around finding Python packages or code to calculate the orbits of time-like and null-like particles in the Schwarzschild metric, specifically in spherical coordinates. Participants are exploring options for visualizing these orbits in the (r, φ) plane and are open to suggestions beyond Python.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Technical explanation, Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant is seeking a Python package to calculate orbits in the Schwarzschild metric, expressing a preference for visualizing results in the (r, φ) plane.
- Another participant suggests searching online, indicating a lack of immediate solutions.
- A participant mentions having tried Einsteinpy but finds it focuses on momentum and initial position rather than energy, expressing uncertainty about the required values for generating the desired graphs.
- Code is shared that utilizes Einsteinpy to plot geodesics, but the participant questions how to produce specific images related to the orbits.
- One participant offers a code snippet for Kerr spacetime, suggesting it can be adapted for Schwarzschild by setting a=0, and expresses willingness to assist further.
- Another participant doubts the ability to extract effective potential from the code but believes it can still generate the orbits.
- There is a request for guidance on how to run the code to produce the desired images.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the capabilities of the code and packages discussed. There is no consensus on a specific solution or method to achieve the desired visualizations.
Contextual Notes
Participants have not reached a resolution on the specific values or parameters needed for the calculations, and there are uncertainties regarding the effective potential and how to run the provided code.