Homework Help Overview
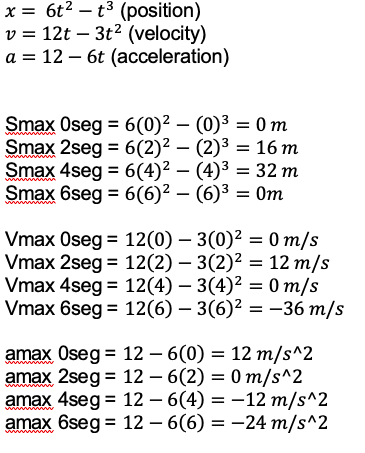
The discussion revolves around the rectilinear movement of a particle, focusing on finding critical points and local extrema using algebraic methods and graphical representation. Participants are exploring the relationship between time, velocity, and position in the context of a second-degree equation.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Conceptual clarification, Mathematical reasoning, Problem interpretation
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants discuss the need for critical points and local extrema, questioning whether to use graphical methods or algebraic approaches. There are attempts to clarify how to interpret results and derive values from equations, particularly regarding the maximum displacement.
Discussion Status
The discussion is ongoing, with participants providing guidance on finding local extrema and checking for maxima. Some participants express uncertainty about the interpretation of results and the graphical representation of the particle's trajectory.
Contextual Notes
There is mention of the teacher's emphasis on critical points and the need for additional graphics, as well as uncertainty regarding the interpretation of the particle's trajectory and the results obtained from the equations.
 PD: I don't know how make a MRU graphic in excel.
PD: I don't know how make a MRU graphic in excel.