Dita
- 3
- 0
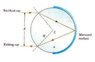
A cylindrical material of radius R = 2.00 m has a mirrored surface on its right half, (as in figure that i have attached below). A light ray traveling in air is incident on the left side of the cylinder. If the incident light ray and exiting light ray are parallel and d = 2.00 m, determine the index of refraction of the material.
I know that the index of refraction of a material n is n = c /u where c is the speed of light in a vacuum and u is the speed of light in the material.
But in the figure there is nothing which has to do with this formula.
A little help?
I know that the index of refraction of a material n is n = c /u where c is the speed of light in a vacuum and u is the speed of light in the material.
But in the figure there is nothing which has to do with this formula.
A little help?