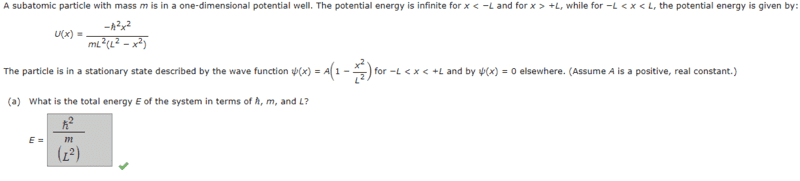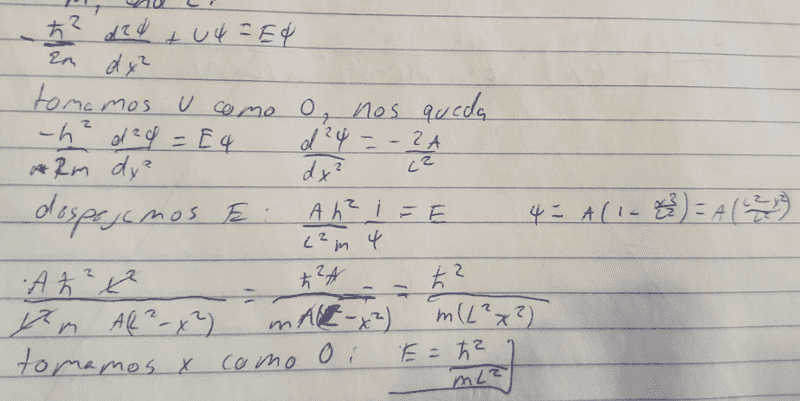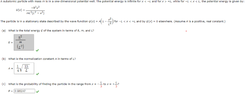Que7i
- 1
- 0
New poster has been reminded to use LaTeX for math equations (not pictures of their work)
- Homework Statement
- A subatomic particle with mass m is in a one-dimensional potential well. The potential energy is infinite for x < −L and for x > +L, while for −L < x < L, the potential energy is given by:U(x) =(−ℏ^2x^2)/(mL^2(L^2 − x^2)
The particle is in a stationary state described by the wave function 𝜓(x) = A(1 − x^2/L^2)
for −L < x < +L and by 𝜓(x) = 0 elsewhere. (Assume A is a positive, real constant.)
What is the total energy E of the system in terms of ℏ, m, and L?
- Relevant Equations
- -ℏ/(2m)d^2𝜓/dx^2+U𝜓=E𝜓
I've already found out how to do it, but, either I got lucky and my procedure is wrong or I just don't get it. Why are U and -x^2 equal 0?