thatboi
- 130
- 20
Hey all,
I am currently trying to solve the following equation for C:
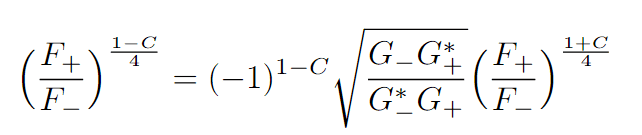
where C is a purely imaginary value, ##F_{+}##, ##F_{-}## and ##G_{+}## and ##G_{-}## are all complex valued constants (so ##G_{+}^{*}## just means complex conjugate of ##G_{+}##. I am not really sure where to start with isolating C, any advice would be greatly appreciated!
I am currently trying to solve the following equation for C:
where C is a purely imaginary value, ##F_{+}##, ##F_{-}## and ##G_{+}## and ##G_{-}## are all complex valued constants (so ##G_{+}^{*}## just means complex conjugate of ##G_{+}##. I am not really sure where to start with isolating C, any advice would be greatly appreciated!