Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around solving situational problems involving trigonometric identities, specifically focusing on the values of sine and cosine derived from a right triangle using the Pythagorean theorem. Participants seek to clarify their understanding and calculations related to these identities.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Mathematical reasoning
- Homework-related
Main Points Raised
- One participant expresses confusion about the problem and requests assistance in solving it.
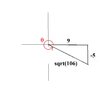
- Another participant calculates $\sin\theta$ and $\cos\theta$ using the Pythagorean theorem, stating $\sin\theta = \sqrt{\frac{|-5|}{106}}$ and $\cos\theta = \frac{3}{\sqrt{106}}$, leading to the expression $\sin\theta + \cos\theta = \frac{3+\sqrt{|-5|}}{\sqrt{106}}$.
- A similar calculation is repeated by another participant, reinforcing the values of $\sin\theta$ and $\cos\theta$ as derived from the triangle's dimensions.
- A different participant presents $\cos{\theta} = \dfrac{9}{\sqrt{106}}$ and $\sin{\theta} = \dfrac{-5}{\sqrt{106}}$, leading to a different expression for the sum of sine and cosine, $\cos{\theta} + \sin{\theta} = \dfrac{4}{\sqrt{106}}$.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants present differing calculations for the sum of sine and cosine, indicating a lack of consensus on the correct values and expressions derived from the triangle's dimensions.
Contextual Notes
Some calculations depend on the interpretation of the triangle's dimensions and the signs of the sine and cosine values, which may not be fully resolved in the discussion.

 )
)