chwala
Gold Member
- 2,833
- 426
- Homework Statement
- See attached.
- Relevant Equations
- separation of variables
I am on differential equations today...refreshing.
Ok, this is a pretty easier area to me...just wanted to clarify that the constant may be manipulated i.e dependent on approach. Consider,

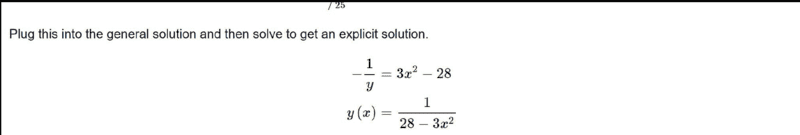
Ok I have,
##\dfrac{dy}{6y^2}= x dx##
on integration,
##-\dfrac{1}{6y} + k = \dfrac{x^2}{2}##
##k= \dfrac{x^2}{2} + \dfrac{1}{6y}##
using ##y(1)=0.04## we shall get,
##k=\dfrac{28}{6}##
##\dfrac{28}{6}-\dfrac{x^2}{2}=\dfrac{1}{6y}##
...
aaargh looks like i will get the same results...cheers
Ok, this is a pretty easier area to me...just wanted to clarify that the constant may be manipulated i.e dependent on approach. Consider,
Ok I have,
##\dfrac{dy}{6y^2}= x dx##
on integration,
##-\dfrac{1}{6y} + k = \dfrac{x^2}{2}##
##k= \dfrac{x^2}{2} + \dfrac{1}{6y}##
using ##y(1)=0.04## we shall get,
##k=\dfrac{28}{6}##
##\dfrac{28}{6}-\dfrac{x^2}{2}=\dfrac{1}{6y}##
...
aaargh looks like i will get the same results...cheers