cool2shiv
- 5
- 0
Hey,
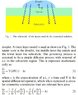
I want to solve a parabolic PDE with boundry conditions by using FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD in fortran. (diffusion) See the attachment for the problem
The problem is that there is a droplet on a leaf and it is diffusing in the leaf
the boundry conditions are
dc/dn= 0 at the upper surface of drop as well as the leaf
and
dc/dz = 0
for the bottom most layer
and the width is taken very large
Can anyone help me please in making the grid for using FDM
the Droplet is not hemispherical in shape.
I want to solve a parabolic PDE with boundry conditions by using FINITE DIFFERENCE METHOD in fortran. (diffusion) See the attachment for the problem
The problem is that there is a droplet on a leaf and it is diffusing in the leaf
the boundry conditions are
dc/dn= 0 at the upper surface of drop as well as the leaf
and
dc/dz = 0
for the bottom most layer
and the width is taken very large
Can anyone help me please in making the grid for using FDM
the Droplet is not hemispherical in shape.