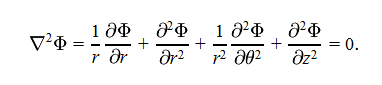SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on solving the Laplace equation using the method of separation of variables. A participant expresses confusion regarding the application of the product rule in differentiation, specifically the formula \(\frac{\partial}{\partial x} \left(f(x)g(x)\right) = g(x) \frac{\partial f(x)}{\partial x} + f(x) \frac{\partial g(x)}{\partial x}\). This mathematical principle is crucial for correctly manipulating functions during the separation process. The conversation highlights the importance of understanding differentiation rules in mathematical problem-solving.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of the Laplace equation and its significance in mathematical physics.
- Familiarity with the method of separation of variables.
- Knowledge of basic calculus, particularly differentiation rules.
- Proficiency in applying the product rule in calculus.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the method of separation of variables in solving partial differential equations.
- Review the product rule and its applications in calculus.
- Explore examples of solving the Laplace equation in various coordinate systems.
- Investigate common pitfalls in differentiation to enhance problem-solving skills.
USEFUL FOR
Mathematics students, educators, and professionals in fields involving differential equations, particularly those focusing on mathematical physics and engineering applications.