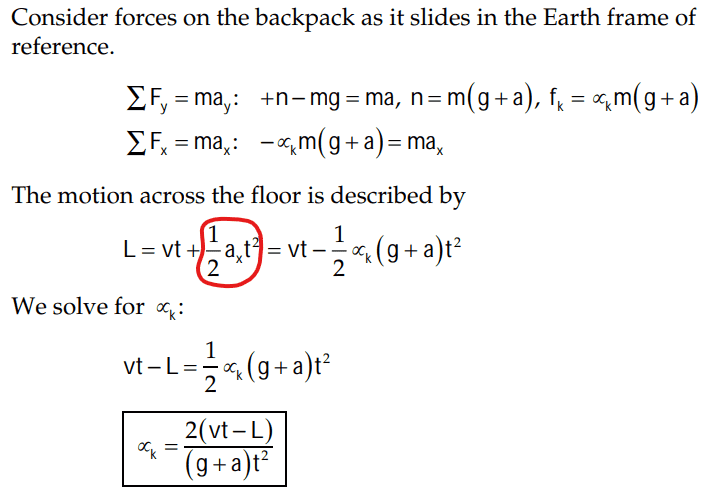SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the physics of a student sliding a bag along the floor of an elevator. The primary equation referenced is ##-0.5a_xt^2##, which is used to analyze the motion under the influence of acceleration. The negative acceleration term, represented as a_x=-\alpha_k (g+a), indicates that the acceleration is directed opposite to the motion. The conversation highlights the importance of correctly interpreting the signs of acceleration in kinematic equations.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of kinematic equations in physics
- Familiarity with the concepts of acceleration and forces
- Knowledge of the coefficient of kinetic friction (α_k)
- Basic grasp of gravitational acceleration (g)
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation and application of kinematic equations in varying contexts
- Explore the effects of friction on motion in different environments
- Learn about the implications of negative acceleration in physics problems
- Investigate the relationship between gravitational forces and motion in elevators
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics, educators teaching kinematics, and anyone interested in the dynamics of motion in non-inertial reference frames.