MarkFL
Gold Member
MHB
- 13,284
- 12
Here are the questions:
I have posted a link there to this topic so the OP can see my work.
Help with solving these quadratic worded problems?
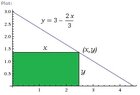
1) A rectangle is constructed so that one vertex is at the origin, and another vertex is on the graph of y=3 - 2x/3 where x >0 and y>0 and adjacent sides are on the axes. what is the maximum possible area of the rectangle?
2) What is the minimum value of 3x^2 +7x -2 if -3 ≤ x ≤ 0 ?
3) What is the maximum value of 3x^2 + 7x - 2 if 0 ≤ x ≤ 3?
I have posted a link there to this topic so the OP can see my work.