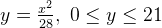Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around calculating the surface area of rotation of a curve about the y-axis, specifically for the curve defined by the equation $$x=\sqrt{28y}$$. Participants explore various approaches to set up the integral for the surface area, including discussions on limits of integration and the application of the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (FTOC).
Discussion Character
- Mathematical reasoning
- Technical explanation
- Homework-related
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant proposes the integral setup for the surface area as $$2\pi\int_0^{21}\sqrt{28y+196}$$ and questions its correctness.
- Another participant suggests rewriting the integral in terms of $$x$$ and provides the formula $$S=2\pi\int_a^b x\sqrt{1+\left[f'(x) \right]^2}\,dx$$, indicating that the limits should correspond to $$y=0$$ and $$y=21$$.
- There is a discussion about the correct application of the FTOC, with some participants expressing confusion over the integration and substitution steps.
- Several participants calculate the integral using different methods, including substitution, and arrive at expressions involving $$\frac{\pi}{21}$$ and powers of $$28$$ and $$14$$.
- One participant expresses uncertainty about the change of the factor $$2\pi$$ during substitution, indicating a lack of clarity on this aspect.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree on the approach to set up the integral for the surface area, but there are multiple competing views on the correct application of integration techniques and the handling of constants. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the final evaluation of the integral and the correct interpretation of the results.
Contextual Notes
Some participants mention confusion regarding the application of the FTOC and the substitution method, indicating that there may be missing assumptions or unclear definitions in the integration process.
 rotate in y-axe.
rotate in y-axe.